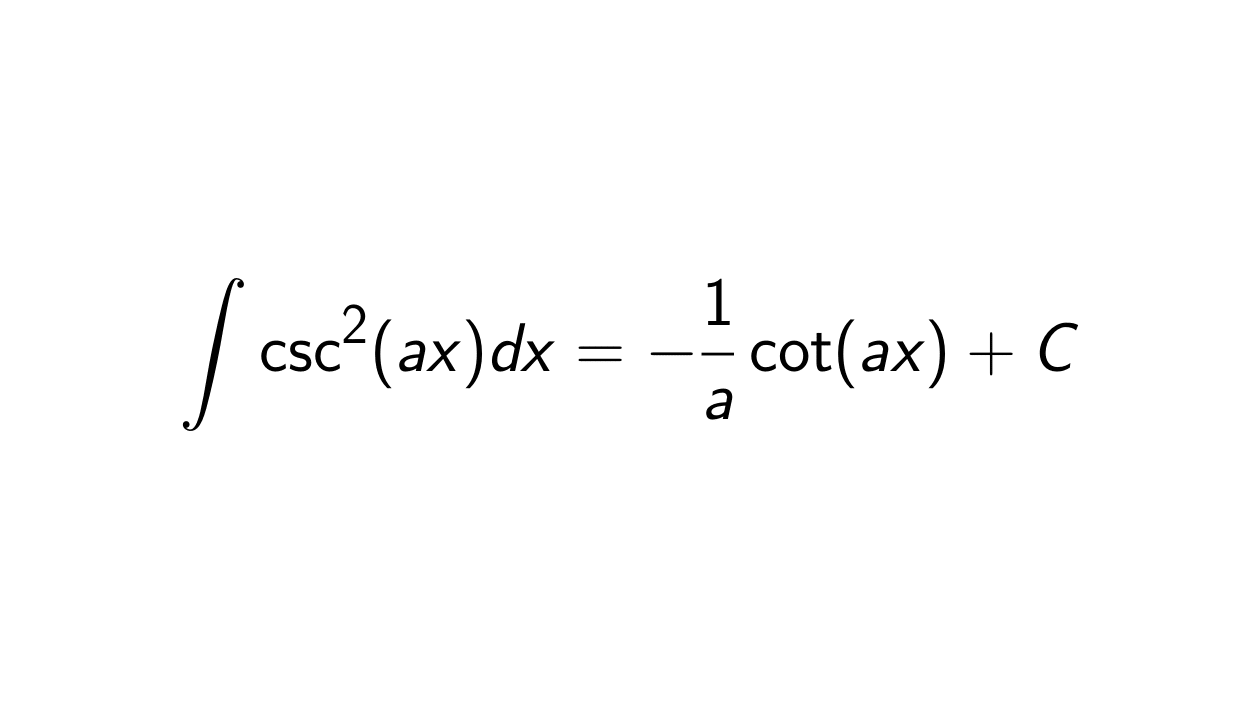The integral of
\csc^2(ax) is
\frac{1}{a}\cot(ax) + C.
Proof. First we want determine the integral of
\csc^2(x), that is:
\begin{align*}
\int \csc^2(x) dx.
\end{align*}
We have seen
here that
\frac{d}{dx} \cot(x) = -\csc^2(x). Now take the antiderivative of
\csc^2(x), which is equal to
-\cot(x). Therefore:
\begin{align*}
\int \csc^2(x) dx = -\cot(x) + C'.
\end{align*}
Lastly, we want to determine the integral of
\csc^2(ax). We now that the following derivative is
\frac{d}{dx} \cot(ax) = -a\csc^2(ax). So we can take the antiderivative of
\csc^2(ax) which results:
\begin{align*}
\int \csc^2(ax) dx = -\frac{1}{a}\cot(ax) + C.
\end{align*}
Therefore, the integral of
\csc^2(ax) is
\frac{1}{a}\cot(ax) + C.